Horticulture Guruji
Tomato Products- Concepts and Standards
Tomato products
Commercial tomato products include juice, puree, paste, ketchup, soup, canned and dehydrated tomatoes. As a semi-finished product, tomato puree is prepared on a small scale while tomato paste is prepared on a large scale. Both puree and paste are used for the preparation of various finished products like ketchup, juice, soup, etc. The methods of preparation of various tomato products are as follows:
Watch Lecture Video
-
Tomato juice/pulp
Ripe and fully red tomatoes are used to make the juice. All green, blemished and overripe fruits should be removed. The yield, colour, and taste of the juice depending on the ripeness and variety of the tomato. Wash tomatoes thoroughly with water. They are crushed by means of a wooden roller-crusher. Tomato juice is either hot or cold pulped. It can also be extracted through a screw-type juice extractor. To neutralize the astringent taste of the juice, 0.4 to 0.6% salt is mixed with the juice. Sometimes sugar is also added to improve the taste. Juice is packaged in glass bottles or cans. Tomato pulp/juice is the basic ingredient for preparing various tomato products like tomato puree, paste, ketchup, etc.
Method for preparation of tomato juice
Washing: Tomatoes should be thoroughly washed under running water to remove dirt from cracks, wrinkles, folds, and cavities of the fruit, which are not easily removed by washing.
Crushing: After sorting the tomatoes are cut into four to six pieces to extract the pulp. Alternatively, they can be crushed through fluted roller crushers or by passing through a fruit grater.
Pulping: Tomato pulp can be extracted either by crushing without heating (cold pulping) or by passing through a pulper after crushing or boiling whole tomatoes until soft. During pulping, the fine juice and pulp passing through the pulp sieve are collected, while the peel and seeds are separated from the other end.
A) Cold Pulping: It is commonly known as the cold break process in which tomatoes are crushed with a fruit grater after being washed and immediately passed through a pulper to extract the pulp. The features of the cold break process are as follows:
- The yield of juice is low as the extraction is comparatively difficult in the cold process.
- The juice extracted is lighter in color because the natural red color of tomatoes is released only after heating the peel.
- The cold break process results in the destruction/oxidation of the natural vitamin C in the juice, due to the incorporation of air during juicing.
- The extracted juice is dilute, possibly due to the action of the pectinase enzyme contained in natural pectin.
- The taste of cold break juice is more pungent and more acidic than that of hot pulp juice.
- Cold pulp juice needs to be processed immediately to avoid the possibility of spoilage by micro-organisms.
B) Hot Pulping: It is also known as the hot break process. After the fruit is grated or grinded, the tomatoes are boiled in a pressure cooker/steam jacketed steel kettle or aluminum pan till soft to make it easier to remove the pulp from the pulper. The properties of hot pulping are as follows:
- Hot pulp extract destroys the enzymes (pectinase) contained in it that would otherwise hydrolyze the pectin, to thicken the extracted juice.
- On heating, the natural lycopene (red color) present in the peel is released into the juice.
- It also partially sterilizes the juice to prevent the growth of micro-organisms.
- It helps in the inactivation of oxidative enzymes which subsequently lead to the destruction of the juice ascorbic acid.
- The juice yield in hot pulping is higher than in cold pulping.
Juice/Pulp Extraction Equipment: Tomato juice/pulp is extracted either by passing crushed tomatoes through a continuous spiral press or pulper.
i) Continuous Spiral Press: It consists of a long spiral screw that presses the tomatoes against a thin screen of fine mesh. The juice passes through the screen while the seeds and rind are removed from the lower end of the sieve.
ii) Pulper: The pulper consists of a horizontal cylinder made of stainless steel. The heavy paddles rotate rapidly inside the cylinder, allowing the finer pulp to pass through the screen/sieve which is collected separately while the rind, seed, fiber pieces, etc. pass through the other end of the machine. However, domestically, crushed tomatoes can be manually filtered through a stainless steel sieve after heating.
Finishing and Homogenization: After extraction, common salt (0.4-0.6%) and sugar (1%) are added to the extracted pulp/juice to improve the taste of the finished product. For commercial production, the liquid juice is mixed with the pulp and homogenized to provide a thick consistency and uniform appearance. For homogenization, the juice is heated to 66°C and forced under high pressure (70 kg/cm2) to shred the particles and bring them to approximately the same size.
Filling: The finished juice is heated to 82-88°C and served in pre-sterilized glass bottles. The bottles are then hermetically sealed using crown corks and sterilized in boiling water (100°C) for about 25-30 minutes. Typically, sterilization times at 100°C are 25 minutes (A2 cans), 30 minutes (A21/2 cans), and 40 minutes (A10 cans) for cans of different sizes.
Labeling and storage: After sterilization, cans are cooled and stored in a cool dry place. The glass bottles are allowed to cool in the air. Both the bottles and cans are labeled before they are sent to market/sale.
-
Tomato Puree
Tomato puree is prepared from tomato pulp after evaporation or concentration of juice/pulp into desired total soluble solids with or without salt. As per the FPO specification, tomato puree must contain at least 9% total soluble solids (TSS) excluding salt. The percentage of total soluble solids is required to be declared at the product level.
Method to make Tomato Puree:
- To make the puree, tomato pulp is prepared from ripe tomatoes using either the hot or cold pulping method.
- The pulp/juice is concentrated either in a steam jacketed kettle using an open cooking method or using a vacuum pan.
- However, vacuum pan cooking is desirable as the juice/pulp boils at a very low temperature (71°C) resulting in retaining the original red colour and flavour along with natural vitamin C.
- The pulp is concentrated to the desired solid (9 to 12% TSS),
- Packaged in pre-sterilized bottles, the crown is corked and processed in boiling water for 25-30 minutes.
- Tomato puree can also be preserved by adding sodium benzoate (250 ppm benzoic acid).
- For packing in tin cans, tomato puree is heated to 82-88°C and then processed at 100°C for 20 minutes after the can is closed.
-
Tomato Paste
Tomato paste is the thick juice or pulp of tomato without the skin and seeds and containing at least 25% tomato solids (TSS). Depending on the degree of concentration, tomato paste can be further divided into three groups:
- Light tomato paste containing 25-29% TSS salt-free tomatoes.
- Medium tomato paste containing 29-33% TSS salt-free tomatoes.
- Heavy tomato paste containing at least 33% TSS salt-free tomatoes.
Method to make Tomato Paste:
- Tomato pulp or juice is concentrated in the open pan to 14-15% soluble solids (TSS),
- It is then concentrated in vacuum pans and packaged in pre-sterilized bottles in a heated state.
- In large-scale processing units, tomato paste is manufactured using vacuum evaporators and packaged in tin cans or bulk aseptic packages.
- Tomato paste is used to manufacture various tomato products like ketchup, soups, sauces, etc.
- Tomato Ketchup
Tomato ketchup is a commercial product made by converting fresh tomato juice/pulp or using tomato puree or tomato paste. It is made by concentrating the juice or pulp of tomatoes without the seeds and rind. Spices, salt, sugar, vinegar, onion, garlic, etc. are added to the extent that the ketchup contains at least 12% tomato solids and at least 25% total soluble solids (w/w). The general method for making tomato ketchup is as follows:
Ingredients for Ketchup
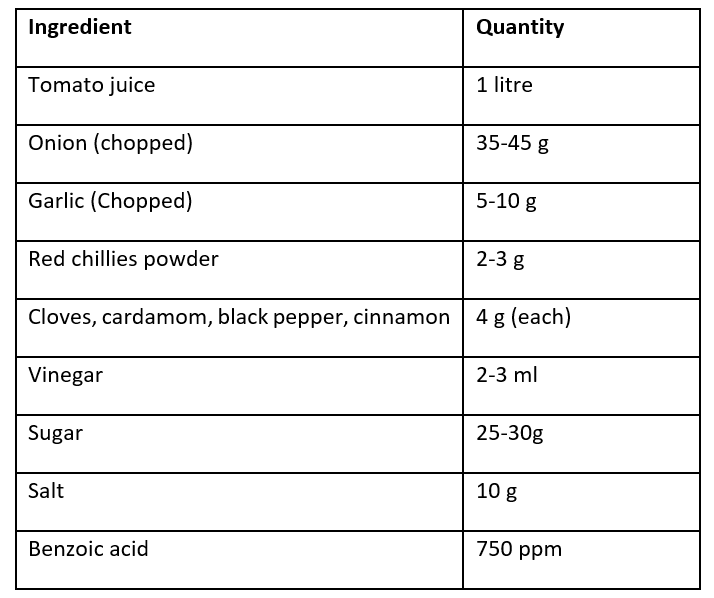
Method to make Tomato Ketchup:
- In tomato ketchup, tomato juice is concentrated with spices, salt, sugar, etc.
- About 1/3 of the sugar is added initially at the time of boiling and the remaining amount is added a little before the ketchup is ready.
- Salt is added at the end of boiling, otherwise, it turns the tomato white.
- The spices are placed in a muslin cloth bundle and the bundle is placed in the boiling mixture. Finally, the cloth bundle is pressed to squeeze out the spices and the bundle is removed.
- Vinegar should be added when the ketchup is thick enough so that the acid does not evaporate. Tomato ketchup usually contains 1.25-1.50% acid.
- Tomato ketchup is typically cooked until it has 25–30% solids, of which 12% are tomato solids.
- Hot ketchup (88°C) is filled into pre-sterilized glass bottles, crown corked and processed for 30 minutes, and cooled to room temperature.
- Benzoic acid is added as a preservative in tomato ketchup.
-
Tomato Soup
Nowadays tomato soup is a very popular product. It can be prepared from pulp or tomato juice. Butter or cream, spices, starch, etc. are used to make soup. These are mixed in different proportions depending on the desired taste. There are many recipes that give tomato soup its best quality.
Ingredients for Soup
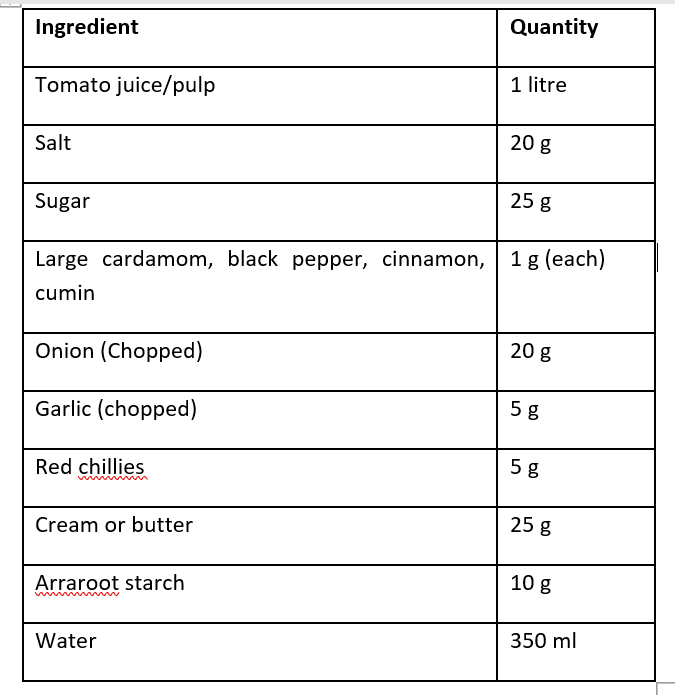
Method to make Tomato Soup:
- The juice is boiled in a pan to concentrate it.
- Put the spices in a cloth bag as in tomato ketchup, and put it in the pan while it cooks.
- Meanwhile, arrowroot and butter are mixed with a small amount of juice to form a smooth paste and then added to the boiled juice.
- It is continued to boil, stirring continuously, until the desired thickening or consistency.
- Finally, adding sugar and salt, the mixture is boiled for about 2 minutes so that it dissolves.
- The hot soup (88°C) is stuffed into cans and processed at 100-110°C for 20-45 minutes depending on the size of the can and quickly cooled down after processing.
-
Tomato Powder
Tomato juice is converted into a free-flowing, highly hygroscopic powder using various drying methods. In powdered form, it can be added to any food to get a natural tomato flavor. The juice can be converted into powder using various methods such as spray drying, roller drying, and foam mat drying.
-
Tomato Cocktail
The tomato cocktail consists of tomato juice mixed with common salt, vinegar, Worcestershire sauce, lime, or lemon juice in varying proportions to suit the taste. It is prepared just before use or sometimes served from stock. The general recipe for a tomato cocktail is as follows:
Ingredients for cocktail
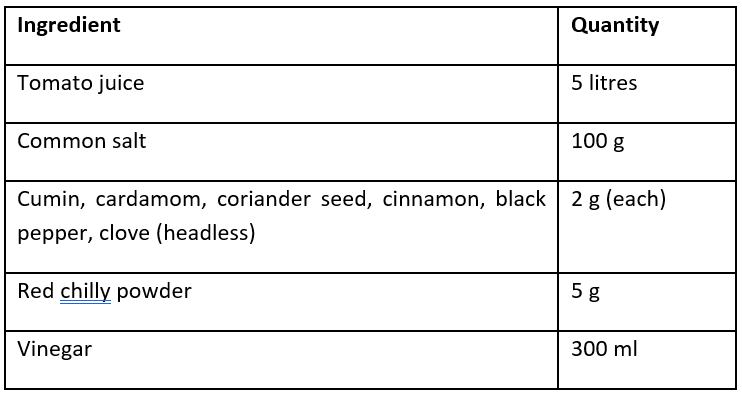
Method to make Tomato Cocktail:
- Boil the tomato juice in a covered pan for about 20 minutes, and tie the spices in a cloth bag, as is done in ketchup.
- When cooked, add vinegar and salt to it.
- The cocktail is ready by mixing all the ingredients and the hot cocktail (88°C) is filled into pre-sterilized glass bottles, crown corked and processed for 30 minutes, and cooled to room temperature.
Problem-making sauce or ketchup
Black Neck: – The formation of black rings in the neck of the bottle is called the black neck. This is due to iron entering the product from the metal of the equipment or from the cap/crown cork and reacting with the acetic acid. Thus iron comes in contact with the tannins of spice to form ferrous tannate which gets oxidized to black ferric tannate. The black neck can be prevented in the following ways:
- Hot sauce should not be filled at a temperature below 85°C.
- The bottle should leave very little space at the top (the more the air, the greater the blackness)
- Reducing contamination from iron.
- Sugar is partially replaced by corn syrup or glucose syrup which contains sulfur and prevents darkening.
- Addition of 100 ppm sulfur dioxide or 100 mg ascorbic acid.
- Holding the bottle horizontally or upside down so that the air (O2) is dispersed throughout the bottle and thereby lowers its concentration sufficiently to avoid darkening of the neck.
- Use cloves only after removing the flower/head.
