Horticulture Guruji
Definition, Importance, and Scope of Fruits and Plantation Crops
Pomology: – The word Pomology is made up of the Latin language word ‘Pomum’ meaning ‘fruits’ and Greek language word ‘logy’ meaning ‘science’ and thus the science of fruit production is called Pomology.
Importance and Scope: –
During 2017-18, the production of horticulture crops was 311.71 Million Tonnes from an area of 25.43Million Hectares. The production of fruits has increased from 50.9 Million Tonnes to 97.35 Million Tonnes from 2004-05 to 2017-18.
Watch Lecture Video Part Ist
Figure 1 (Production in MT)
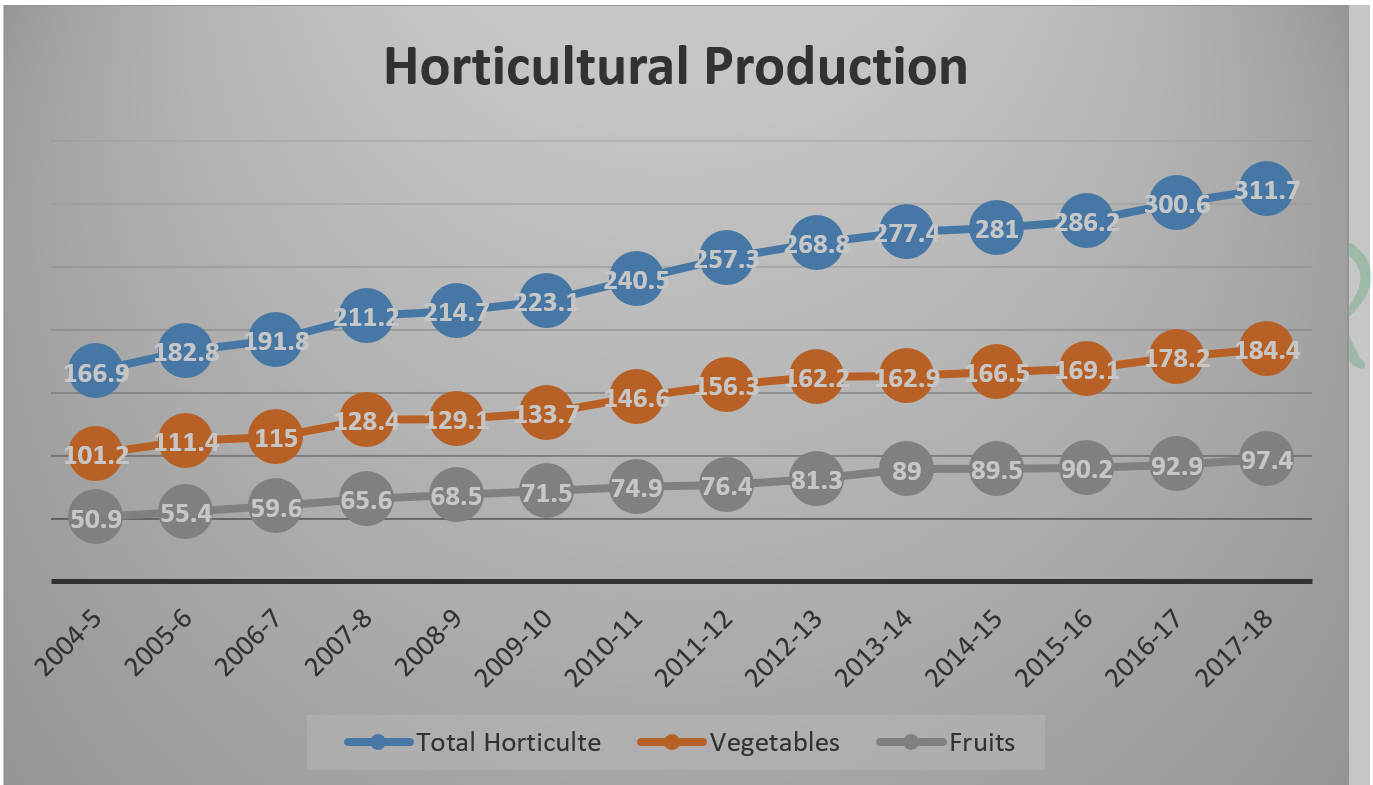
Figure 2 (Share in percentage)
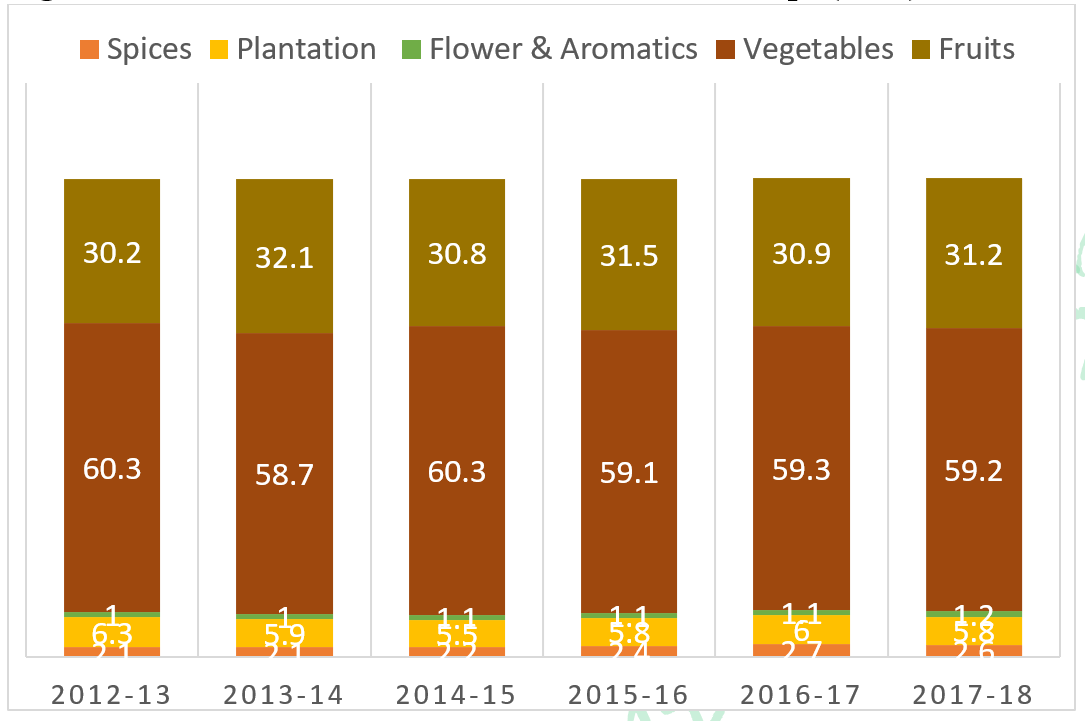
Table:- Area, Production, and Productivity of Horticultural Crops
|
Crops |
Area (000,ha) |
Production (000,MT) |
Productivity (MT/ha) |
|
Fruits |
6506 |
97358 |
14.96 |
|
Vegetables |
10259 |
184394 |
17.97 |
|
Flowers, Medicinal and Aromatic Crops |
1044 |
3651 |
3.49 |
|
Plantation Crops |
3744 |
18082 |
4.83 |
|
Spices |
3878 |
8124 |
2.09 |
|
Total |
25431 |
311714 |
12.25 |
- India is the second-largest country in fruit production in the world and China ranks first in production.
- India ranks first in mango, banana, coconut, cashew nuts, papaya, and pomegranate production and the productivity of some fruits is also very high like papaya, banana, etc.
- It is estimated that per capita fruits availability in our country is 207.9 gms. per day which is far below the recommended quantity of 230 gms. per capita per day
- Plantation crops are another potential sector with a lot of opportunities for employment generation, foreign exchange earnings, and overall supporting livelihood sustenance of mankind at large.
The importance of horticulture is as follows
1. Income generation: – More money can be earned by selling fruits, and plantation crops as they have a higher yield per hectare.
2. Employment Generation: – Horticulture crops require workers throughout the year, from growing crops to harvesting and processing, so garden crops create more jobs.
3. Industrial development: –Horticultural crops mangoes, grapes, and plantation crops give raw materials to factories. These factories make products from them and sell them in the market.
4. Religious and sacred value: –Tree leaves, flowers, fruits, etc., are of religious importance which is used in rituals, sanskars, and ceremonies. As coconut is used in puja, the leaves of the Beal are offered to Lord.
5. Food value: – Some fruits such as cashew nuts, almonds, walnuts are rich in fats and proteins, and in many areas, potatoes and bananas are used as staple foods that can meet all the needs of the body.
6. Nutritional value: – Fruits and vegetables are rich in nutrients so the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has recommended 120 grams of fruits to be eaten by each person every day. The nutrient fruit is as follows:
-
Vitamin A
Mango (4800 IU/100gm)> Papaya (2020 IU/100g)
-
Vitamin B (Thiamine)
Cashew nut (630mg/100gm) > Walnut (450mg/100gm) > Apricot (dry) (217mg/100)
-
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
Beal(1191mg/100gm) > Papaya (250mg /100gm) > Litchi (122.5mg /100gm)
-
Vitamin C
Barbados cherry (1000-4000mg /100gm) >Aonla (600mg/100gm) > Guava (299mg / 100gm)
-
Carbohydrat
Apricot (dry) (72.81%) > Date (Pind) (67.30%) > Karonda (dry) (67.10%)
-
Protein
Cashew nut (21.20%) > Almond (20.80%) > Walnut (15.60%)
-
Fat
Walnut – (64.50%) > Almond (58.90%) >Cashewnut (46.90%)
-
Fibre
Guava(6.90%) >Kaintha (5.20%) > Pomegranate (5.10%) >Aonla (3.40%)
-
Phosphorus
Cashewnut (0.45%) > Walnut (0.38%) > Litchi – (0.30%)
-
Iron
Karonda (dry) (39.1%) > Date (pind) (10.6%) >Cahewnut (5.0%)
-
Calcium
Litchi (0.21%) > Karonda (dry) (0.16%) >Kaintha (0.13%)
7. Aesthetic value: –Many kings considered the trees as symbols of being young and planted them in the palace. Mughal emperors have given great importance to fruit trees and flowers in the styles of their gardens. They considered the cypress plant a symbol of death and planted it around the tombs. In the cities, fruit trees are planted on both sides of the road called avenue planting.
8. Export Value: –Indian products are in great demand abroad mango, grapes, etc. are exported from India. Exporting these products gives foreign exchange to the country.
References cited
- Commercial Fruits. By S. P. Singh
- A text book on Pomology, Vol,1. by T. K. Chattapadhya
- Tropical Horticulture, Vol.1, by T. K. Bose, S. K. Mitra, A. A. Farooqui and M. K. Sadhu
